Thermal Deformation Analysis in Surface Thermal Lensing via COMSOL Multiphysics
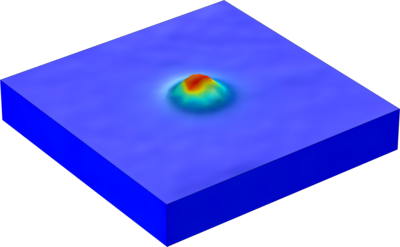
This study investigates the thermal deformation process in Surface Thermal Lensing (STL), a non-destructive technique used to characterize optical materials based on their absorption properties. A fused quartz sample (10mm10mm3.3mm) was modeled with adiabatic free boundaries on the upper and lower surfaces and fixed constraints on the sides. A Gaussian pump beam was vertically incident along the z-axis, generating a periodic temperature field and resulting in periodic thermal deformation on the sample surface. Numerical simulations were performed to analyze the thermal deformation under varying absorption coefficients and the presence of internal defects such as cavities.
The research highlights two key aspects: First, the maximum surface deformation height (below 200 nm) exhibits a strong linear relationship with the absorption coefficient, confirming the suitability of STL for absorption detection. Second, while stress and deformation follow a Gaussian distribution in defect-free samples, the presence of cavities leads to significant stress concentration and enhanced deformation, providing a theoretical basis for defect detection using STL.
COMSOL Multiphysics was employed to simulate the coupled thermal and structural mechanics processes. The Heat Transfer Module and Structural Mechanics Module were used to model the temperature field and thermal deformation, respectively. The study demonstrates how COMSOL efficiently handles multi-physics coupling to optimize measurement accuracy and support the development of improved assay protocols for high-performance optics.