Towards a Predictive Framework for Filter Clogging in Hypolimnetic Withdrawal and Treatment Systems
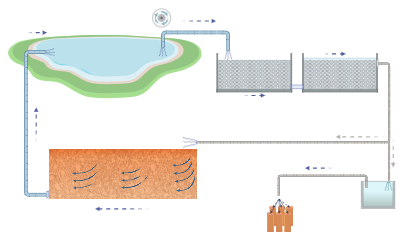
Hypolimnetic withdrawal is a lake restoration technique that targets internal nutrient loading by extracting water from the anoxic hypolimnion, where phosphorus is released from sediments. This method is currently implemented at Lake Kymijärvi in Lahti, Finland, where hypolimnetic water is pumped through a treatment system comprising filtration units and a constructed wetland before being returned to the lake. However, the system’s primary sand filter tends to clog rapidly due to the accumulation of precipitated solids, significantly limiting its operational lifespan.
This study aims to provide a conceptual framework to support the creation of a numerical model capable of simulating porosity and permeability loss in filter materials over time. A two-dimensional model will be built using COMSOL Multiphysics and MATLAB LiveLink. The model will incorporate chemical reactions responsible for phosphorus retention and coprecipitation with ferrihydrite, implemented through the Chemical Reaction Engineering interface. Water flow and solute transport through the porous media will be described using the Subsurface Flow Module.
To capture filter clogging dynamics, mathematical functions will relate porosity changes to the mass and volume of accumulated precipitates, allowing for the estimation of operational longevity. The modeling approach builds upon the methodologies of Samsó and Garcia (2013) and Hamisi et al. (2019), among others.